intervertebral disc mechanical test compression|mechanobiology of the disc : fabrication The aim of the presented study is to review, with a systematic approach, the existing literature regarding the mechanobiology of the human intervertebral disc (IVD), define . Resultado da Edf. Do Casino da Póvoa de Varzim, 4490-403 Póvoa de Varzim. O Casino da Póvoa é um casino localizado na Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal. É um local de jogos e entretenimento desde o início dos anos 1930, e o edifício segue um estilo modernista inspirado por Garnier. Desde 1977, é classificado .
{plog:ftitle_list}
3 de mai. de 2023 · Lazio x Sassuolo ao vivo: escalações, palpites e onde assistir o Campeonato Italiano. Lazio e Sassuolo entram em campo pelo Campeonato Italiano (Série A), às 16:00 (de Brasília), nesta quarta-feira (03 de maio). Portanto, veja as provávei escalações e saiba como assistir o jogo ao vivo, na TV, online e em qual canal vai passar.
The aim of the presented study is to review, with a systematic approach, the existing literature regarding the mechanobiology of the human intervertebral disc (IVD), define .
In vitro mechanical testing of intervertebral discs (IVDs) provides a valuable tool for investigating mechanisms of disc injury and degeneration, mechanical integrity of biological .Many mechanical and chemical events take place in the IVD under compression. For example, fluid pressurization is one of major mechancial events, especially in the NP region, when the .This review aims to summarise recent knowledge on the effects of mechanical loads on the IVD and the disc cells, taking into consideration the changes that IVDs undergo during ageing and . The intervertebral disc acts as a shock absorber and allows flexibility to the spine through a whole range of motions due to its unique structure. Anatomy of the intervertebral disc, the biomechanical properties of .
Our objective was to noninvasively evaluate the internal deformations of nondegenerate and degenerate human discs under axial compression with flexion, neutral, and extension .
mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc
mechanobiology of the disc
This research provides a standardized test protocol for the comparison of spinal specimens and provides steps towards understanding how location and test set-up may affect . In this paper, we investigated the strain rate-dependent mechanical behavior of lumbar intervertebral discs under tensile and compressive loading and used nonlinear . This review focused on specific factors relating to the in vitro mechanical testing of injectable biomaterials for intervertebral disc degeneration, namely the testing approach, .where Q + is the chemical reaction rate for sodium, Q − is the rate for chloride, and Q F is the rate for the fixed charge density with Q F = 2Q GAG because of Eq. (5). Thus, the biological, chemical, electrical, and mechanical events are coupled in the disc. The geometry of the disc used in this study was extracted from a non-degenerated human L2-3 disc (male, non-degenerated), with .
1. INTRODUCTION. Back pain, one of the most common reasons for doctor visits and the leading cause of disability, has been associated with degeneration of the intervertebral discs. 1–3 The intervertebral disc (IVD), the connective tissue between vertebral bodies, is a complex load bearing composite tissue populated by a relatively low density of . The test specimens were divided into 3 groups. In the total mechanical test group, 15 spinal specimens were taken to test the mechanical properties of the disc under different strain rates. In the. Mechanical behavior of the intervertebral disc under tension. Fig. 4 shows the tensile and compressive fracture curves at three speeds. Between each vertebral body of the spine are pads of fibrocartilage-based structures that provide support, flexibility, and minor load-sharing, known as the intervertebral discs. These are primarily composed of two layers: (1) a soft, pulpy nucleus pulposus on the inside of the disc and (2) a surrounding firm structure known as the annulus fibrosus. A .
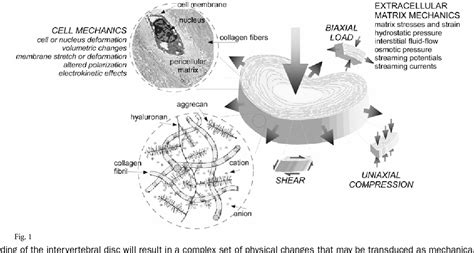
Med Biol Eng Comput 42(1):55–60 25. Roberts S, Menage J, Eisenstein SM (1993) The cartilage endplate and intervertebral disc in scoliosis: calcification and other sequelae. J Orthop Res 11(5):747–757 26. Stokes IAF, Aronsson DD, Spence H, Iatridis J (1998) Mechanical modulation of intervertebral disc thickness in growing rat tails. Intervertebral disc (IVD) is the largest avascular structure in the human body with the nucleus pulposus (NP) being centered and surrounded on its periphery by the annulus fibrosus (AF), and superiorly and inferiorly by cartilaginous endplates (CEP) (Fig. 1).The NP is composed from randomly oriented collagen fibrils enmeshed in a proteoglycan gel while the .
mechanical stimulation of discs
CHAPTER 78 Biomechanics of the Intervertebral Disc Dawn M. Elliott, Chandra S. Yerramalli, Joshua D. Auerbach INTRODUCTION: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF DISC The intervertebral disc separates the rigid vertebral bodies and allows for large, complex, three-dimensional motion of the spine. The disc, therefore, must be soft enough to permit spinal . Degenerative disc disease is one of the most common ailments severely affecting the quality of life in elderly population. Cervical intervertebral body fusion devices are utilized to provide stability after surgical intervention for cervical pathology. In this study, we design a biomimetic porous spinal cage, and perform mechanical simulations to study its performances .
A herniated disc in the spine is a condition during which a nucleus pulposus is displaced from intervertebral space. It is a common cause of back pain. The patient's who experience pain related to a herniated disc often remember an inciting event that caused their pain. Unlike mechanical back pain, herniated disc pain is often burning or stinging, and may radiate into .The effects of four permutations of disc compression, angulation and reduced mobility were studied to identify possible causes of progressive disc deformity in scoliosis. . The purpose of this study was to document morphological and biomechanical changes in four different models of altered mechanical environment in intervertebral discs of .with fetal bovine serum (FBS) as the control. Injected intervertebral discs were exposed to two mechanical tests: flexion/extension and axial rotation. The proposed third mechanical test of compression was not performed. This research was completed in order to develop a viable model of intervertebral disc degeneration in vitro that could be . sciatica symptoms result from combined mechanical compression and associated inflammation. not all patients with mechanical compression develop symptoms . weak evidence to support DMARDs for treatment. Anatomy. Complete intervertebral disc anatomy and biomechanics. Disc composition. annulus fibrosis. composed of . Kernig test. .
is realtor test hard
LI et al. carried out low, medium and high-rate loading of the intervertebral disc, and after observing the mechanical differences in intervertebral disc rupture, . which can better predict the stress–strain curve in the 1.25% strain range under the dynamic compression test with strain rate of 1.45 × 10 −6 s −1, .Degenerative Changes in Structural Properties of the Motion Segment. The function of the motion segment is to provide the spine with axial stability while allowing mobility. 52 The intervertebral disc is responsible for carrying enormous amounts of compressive loading while maintaining flexibility. 53 The load on the disc is mainly compressive, but it is also subjected to other types . A herniated disc in the spine is a condition during which a nucleus pulposus is displaced from intervertebral space. It is a common cause of back pain. The patients who experience pain related to a herniated disc often remember an inciting event that caused their pain. Unlike mechanical back pain, herniated disc pain is often burning or stinging and may .Intervertebral disc disease is a common condition characterized by the breakdown (degeneration) of one or more of the discs that separate the bones of the spine (vertebrae), causing pain in the back or neck and frequently in the .
The primary function of the disc is mechanical; therefore, degenerative changes in disc mechanics and the interactions between the annulus fibrosus (AF) and nucleus pulposus (NP) in nondegenerate and degenerate discs are important to functional evaluation. . Human intervertebral disc internal strain in compression: the effect of disc region . The effect of intervertebral disc damage on the mechanical strength of the annulus fibrosus in the adjacent segment . (3600 cycles). Post compression, the C3/4 AF was dissected to obtain two multilayer samples (one anterior and one posterior) as well as a peel sample (from the posterolateral region). A tensile strength test was conducted to . Spacing of vertebrae: The intervertebral disc helps maintain the spacing between adjacent vertebrae, preventing them from compressing on each other and causing nerve compression or other spinal problems. Nutrient supply: The intervertebral disc contains a network of blood vessels and nerves that provide nutrients to the surrounding tissues .
However, several models of degeneration have been developed in which the animals’ spines or tails are subjected to an extreme mechanical environment.25 These mechanical interventions on the spine, which include forced bipedalism and bending of tails, cause morphologic changes in the disc and vertebrae similar to degenerative disc disease in . 1. Introduction. In vitro mechanical testing of intervertebral discs (IVDs) provides a valuable method in elucidating the biomechanical properties of natural IVDs, including visco-elasticity and poro-elasticity, which are closely related to disc degeneration and help with the development of bionic IVD prostheses with mechanical mimicry [].However, due to the .
The nucleus pulposus is the first disc substructure to exhibit degenerative changes: the shear stiffness increases, 18 the pressure decreases, 15 the compression stiffness increases, 16 the permeability decreases, 16 and its compositional changes lead to a shift from a fluid-like behavior to a solid-like behavior. 17 When the nucleus is .Objective: In this study, the strain rate sensitive and tension-compression asymmetry of the intervertebral disc were analyzed by experiments and constitutive equation. Method: The Sheep intervertebral disc samples were divided into three groups, in order to test the strain rate sensitive mechanical behavior, and the internal displacement as . The second finding was that fatigue load had a certain effect on the internal displacement distribution in the flexed intervertebral disc under compression. Middle AF exhibited the smallest axial . Presumably, axial compression released interstitial fluid from the specimens, thereby leaving the intervertebral disc more viscous than before axial compression was applied. Interestingly, the NZ magnitude after the seven hour compression period was remarkably similar for both methods: the magnitude was the same (1.96° p = 0.98) and they .

Cyclic axial compression of motion segments resulted in failure of the vertebral endplate and . Soaked control specimens were harvested from tissue adjacent to the mechanical test specimens and treated identically to loaded specimens without mechanical testing. . Mechanisms for mechanical damage in the intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus .compression, immobilization, intervertebral disc degen-eration, mechanical modulation] Spine 1999;24:996–1002 Mechanical factors are often associated with disc degen-eration and low back pain. The development of lumbar disc rupture is reported to be associated with activities that involve frequent bending and twisting and heavy
lumbar disc pressure in vivo
WEBOnline casino Free credits offer new players the opportunity of placing bets on several casino games and winning great prizes. In Malaysia, the bonus is referred to as free money or free chips. You can play your favorite .
intervertebral disc mechanical test compression|mechanobiology of the disc